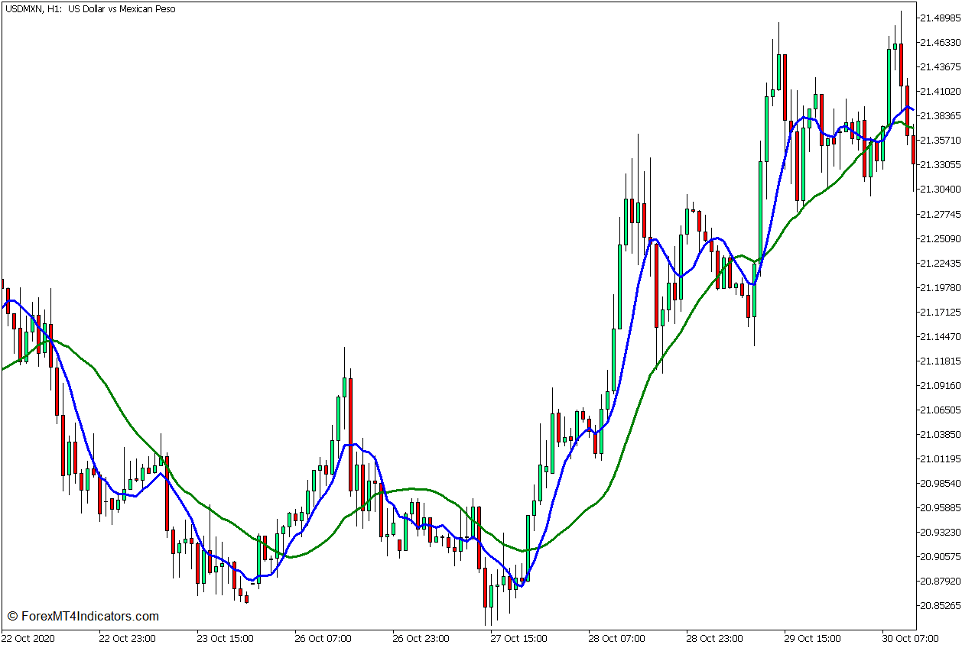
Are you having trouble understanding forex market trends? Feeling lost in the price changes? You’re not alone. Many traders struggle every day. The market’s constant noise can confuse you, leading to big mistakes.
But there’s a powerful tool to help: moving average analysis. This technical indicator clears the confusion, showing clear trends. It gives you a strong base for your trading choices.
Moving averages make price data clearer, showing market direction. They’re flexible, fitting many trading styles and timeframes. Learning moving average analysis gives you a big advantage in forex trading. It helps you spot trends early and make better choices.
Key Takeaways
- Moving averages smooth out price fluctuations in Forex.
- They help identify trends and market direction.
- Common types include Simple Moving Average (SMA) and Exponential Moving Average (EMA).
- Moving averages work across different timeframes.
- They’re essential for developing effective trading strategies.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Moving Averages
Moving averages are key in forex trading. They help smooth out price changes and find trends. Let’s look at how these tools can improve your trading.
What is a Moving Average?
A moving average averages past closing prices over time. It makes trends clearer by reducing market noise. The simple moving average (SMA) treats all prices equally. The exponential moving average (EMA) focuses more on recent prices.
Types of Moving Averages
Forex trading uses two main moving averages:
- Simple Moving Average (SMA): Averages past prices evenly
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA): Gives more weight to recent prices
Both help spot trends. But EMA reacts quicker to price changes because it values recent data more.
Role in Trend Identification
Moving averages are vital for finding trends in forex. If the price is above the moving average line, it’s an uptrend. If it’s below, it’s a downtrend. The trend’s strength depends on the moving average’s timeframe.
| Moving Average Type | Trend Indication | Responsiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Moving Average (SMA) | Slower, smoother trend | Less responsive to price changes |
| Exponential Moving Average (EMA) | Quicker trend signals | More responsive to recent price changes |
Knowing these basics helps traders use moving averages well. They can spot trends and create strong trading plans in the forex market.
Simple Moving Average (SMA) vs Exponential Moving Average (EMA)
Moving averages are key in forex trading. We have a Simple Moving Average (SMA) and an Exponential Moving Average (EMA). Let’s look at how they’re calculated and used.
Calculating SMA and EMA
Calculating SMA is easy. For a 10-day SMA, add the last 10 days’ closing prices and divide by 10. If the total is $150, the SMA is $15. EMA is more complex. It weighs recent prices more. For a 10-day EMA, the latest price gets an 18.18% weight.
Key Differences and Applications
EMA reacts faster to price changes, making trades quicker. SMA gives a smoother trend line. Traders use 50 and 100-day averages for long-term views. A “death cross” happens when the 100-day MA goes below the 200-day MA, showing a possible downturn.
Choosing Between SMA and EMA
Your choice depends on your trading style. Short-term traders like EMA for its quick response. Long-term investors prefer SMA for its stability. It’s good to use both. Use 8 and 20-day EMAs for short-term trends and 50 and 200-day SMAs for long-term trends.
| Feature | SMA | EMA |
|---|---|---|
| Calculation | Equal weight to all prices | More weight to recent prices |
| Responsiveness | Slower | Faster |
| Common Periods | 50, 200 days | 8, 20 days |
Moving Average Analysis in Forex
Moving averages are key in forex market analysis. They give traders a clear view of currency trends. This helps with trend identification and understanding price action. In the fast-changing world, these tools are very helpful for making smart choices.
The 50-day and 200-day moving averages are favorites among traders. The 50-day MA shows short-term trends. The 200-day MA signals when the market might change direction. Traders often use both to see the whole market picture.
There are many moving averages for different trading styles. The Simple Moving Average (SMA) is easy to use. The Exponential Moving Average (EMA) focuses more on recent prices. For example, a 5-day SMA with prices 1, 1.2, 1.5, 1, 1.3 would be 1.2.
More advanced averages like Double and Triple Exponential Moving Averages aim to be more accurate. The EMA Angle Forex Trading Strategy uses these benefits.
Moving averages are also important in other indicators. The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) uses the difference between a 26-day and 12-day EMA to find trading signals.
When using moving averages in forex trading, it’s important to look at different timeframes. Also, use other tools for a complete trading strategy.
Essential Moving Average Trading Strategies
Moving averages are key tools in forex strategies. They help traders spot trends and generate trading signals. Let’s explore three powerful MA-based approaches that can enhance your forex trading.
Single MA Crossover Strategy
This strategy uses price crossovers of a single moving average to create buy and sell signals. When the price crosses above the MA, it’s a buy signal. A cross below suggests selling. The 10 and 20 EMA are popular for this method.
Double MA Crossover Method
This technique involves two moving averages of different periods. When the shorter MA crosses above the longer one, it signals an uptrend. The reverse indicates a downtrend. Traders often use combinations like 10 and 20 EMAs for short-term trades or 50 and 200 SMAs for longer-term analysis.
Moving Average Ribbon Strategy
The ribbon strategy employs multiple MAs to confirm trends and spot possible reversals. It typically uses about 10 MAs of varying timeframes. When the lines fan out, it suggests a strong trend. Converging lines may signal a weakening trend or possible reversal.
| Strategy | Signal Type | Typical MA Periods |
|---|---|---|
| Single MA Crossover | Price-MA Intersection | 10, 20 EMA |
| Double MA Crossover | Short MA-Long MA Intersection | 10/20 EMA, 50/200 SMA |
| MA Ribbon | Multiple MA Convergence/Divergence | 10 MAs of varying periods |
These strategies offer diverse ways to analyze forex markets. Remember, combining them with other indicators can improve your trading accuracy.
Moving Average Envelopes and Bands
MA envelopes help traders see price changes in forex. They have lines above and below a moving average. This makes a channel for price action. Let’s look at how to use these tools well.
Setting Up MA Envelopes
To make MA envelopes, start with a simple moving average (SMA). Then, add bands above and below it. For example, with a 10-day SMA and 2% envelope:
- Upper envelope = SMA + (SMA × 0.02)
- Lower envelope = SMA – (SMA × 0.02)
Trading with Percentage Bands
Percentage bands show when to buy or sell. When prices hit the upper band, it might be overbought. When they hit the lower band, it might be oversold. Traders use these points to decide:
- But when the price closes below the lower band
- Sell when the price closes above the upper band
Support and Resistance Levels
MA envelopes can be supported and resistant. In strong trends, prices often bounce off them. For example, in an uptrend, the lower band is supported. In a downtrend, the upper band is resistance. These levels change with the market, helping traders in forex.
MACD and Moving Averages
The MACD indicator is key in momentum trading and checking trend strength. It was created by Gerald Appel in 1977. This tool mixes two exponential moving averages (EMAs) for a strong analysis method for forex traders.
The MACD uses a 12-period and a 26-period EMA, plus a 9-period signal line. When the MACD line goes above the signal line, it shows a buy chance. Going below the signal line means it’s time to sell.
Traders often use the MACD with other moving average strategies. This helps confirm trends and spot reversals. For example, the Three Moving Averages and MACD strategy uses EMAs of 5, 15, and 50, plus the MACD indicator.
| Currency Pair | Timeframe | Take Profit (pips) |
|---|---|---|
| EUR/USD | H4 | 1000 |
| EUR/USD | D1 | 2000 |
| GBP/USD | H4 | 1250 |
| GBP/USD | D1 | 2500 |
Even though the MACD is great for checking trend strength, it’s a lagging indicator. Traders should use it with other technical analysis methods. This helps make better decisions in the forex market.
Time Frames and Period Selection
Choosing the right timeframe for moving average analysis is key in forex trading. Different MA periods help traders spot trends and make informed decisions. Let’s explore how it impacts trading strategies.
Short-term vs Long-term Averages
Short-term averages react quickly to price changes. Long-term averages smooth out market volatility. Traders use short-term MAs like 9, 10, and 20 days for quick trades.
Long-term averages, such as the 200-day MA, show yearly trends. The choice depends on your trading style and goals.
Optimal Periods for Different Markets
Selecting the best MA periods varies based on market conditions. In calm markets, longer periods work well. But in volatile markets, shorter periods catch quick changes.
The Volume Weighted Moving Average (VWMA) is great for spotting breakouts in high-volume situations.
Multiple Timeframe Analysis
Using multiple timeframes gives a fuller picture of market trends. The “rule of four” helps pick the right mix:
- Medium-term: Your average trade duration
- Short-term: At least 1/4 of the medium-term
- Long-term: At least 4 times the medium-term
This approach helps balance short-term noise with long-term trends. It leads to better trading choices.
| Trading Style | Timeframes | MA Periods |
|---|---|---|
| Scalping | 1-min, 5-min, 15-min | 5, 10, 20 |
| Day Trading | 15-min, 1-hour, 4-hour | 20, 50, 100 |
| Swing Trading | 4-hour, Daily, Weekly | 50, 100, 200 |
Common Moving Average Trading Mistakes
Trading errors can hurt your forex performance. It’s key to know these mistakes for better risk management and market analysis. Let’s look at some common errors traders make with moving averages.
Over-reliance on Single Indicators
Many traders only use moving averages. But, 80% of traders who ignore the bigger picture lose money. Those who only use moving averages make wrong trade entries three times more often.
Ignoring Market Context
Not looking at the bigger picture can lead to bad choices. Traders who ignore the whole market are 25% more likely to lose. It’s important to use moving averages with other tools.
Poor Period Selection
Choosing the wrong moving average period can give wrong signals. Short-term averages can be wrong up to 60% of the time in fast-changing markets. Long-term averages might be too slow, missing market changes by 40%.
| Mistake | Impact | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Over-reliance on Moving Averages | 3x higher incorrect trade entries | Use multiple indicators |
| Ignoring Market Context | 25% increase in loss trades | Integrate broader market analysis |
| Poor Period Selection | Up to 60% false signals in volatile markets | Adjust periods based on market conditions |
By avoiding these mistakes, traders can get better at managing risk and analyzing the market. Remember, moving averages help, but they’re not the only way to trade successfully.
Conclusion
Moving averages are key tools for forex traders. They help in analyzing the market and planning strategies. These tools show trends and when the market might change.
The Simple Moving Average (SMA) and Exponential Moving Average (EMA) are both important. The SMA is easy to calculate, while the EMA is more sensitive to recent prices. Traders use these together to spot trend changes and find good times to buy or sell.
Using moving averages alone is not enough. Successful traders mix them with other tools and know the market well. They adjust their strategy as needed. By learning and improving, traders can use moving averages to make money consistently.